In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, the income for both rural- and urban-based agents has significantly reduced in Uganda because transactions have markedly reduced. Customers cannot travel due to restrictions and they are not transacting as much. With the advent of shared agent network,Ugandans can now easily access banking services irrespective of which agents they visit.These agents can serve customers from several institutions and are able to do more business.
| Agency banking is the delivery of financial services outside conventional bank branches through sub-contracted vendors known as bank agents. A licensed financial service provider contracts a third-party operator (the agent) to provide a range of financial services on behalf of the financial service provider (the principal). We at MSC, are proud to have supported many of the leading banks in Uganda to develop and deploy agency networks. |
In January 2016, the Ugandan Parliament approved the Financial Institutions Act (Amendment) 2016 and thus paved the way for agency banking in Uganda. Furthermore, with the advent of shared agent network Ugandans can now easily access agency banking services irrespective of which providers’ agents they visit.
Considering the massive investment required to set up and manage agency banking structures, Ugandan Banks – under their umbrella association the Uganda Bankers’ Association (UBA)– agreed to set up a shared agency network. The shared agent network operates on a platform jointly owned by the UBA and Eclectics International (a technology service provider)and managed by the Agent Banking Company (ABC).
As of February 2020,13 banks were on ABC’s shared agent platform. As at September 2019, there were 9,477 shared agents spread across the country. These agents facilitated an average of 2.15 million transactions monthly. Agents on the shared platform can facilitate deposits, withdrawals, utility bill payment, open accounts, do balance inquiries, provide mini statements, and handle school fees payments.
Benefits of the shared agent network
The key benefit for the participating banks that shared agent networks bring is the cost-saving. The banks have saved on the investment required to set up their individual agent networks. The costs of setting up and managing agent networks include the hardware (point-of-sale devices, smartphones, and blue tooth printers), recruitment and onboarding, and training.

The shared agent network in Uganda rides on existing networks of some of the largest financial service providers (in terms of outreach in the market) and hence is able to expand the network’s presence and increase transactions. In addition, the agents benefit from simpler float management.
Agents can now rebalance at any bank branch at a cost which is 30% of the regular cash withdrawal fee, regardless of whether the transaction was a withdrawal or deposit. Float re-balancing is an extra income stream that encourages the banks to open up their branches to agents of other banks.
The shared agent platform is more thana switch. It is a robust platform that can – in addition to cash-in/cash-out –offer:digitalon-boarding, utility payments, bulk payments, fund transfers, amongst others. The UBA is encouraging banks to incrementally offer all these services through the shared agent network.
Through the agency banking channel, banks have managed to push basic transactions out of,and thus reduce congestion at, their branches. In an interview with NBS Television in 2019, the Head of Agent Banking at Stanbic Bank, Ronald Muganzimentionedthat 85% of the basic transactions at Stanbic are now happening outside the branches. This is partly attributed to being on the shared platform.
Some of the agents who had agency banking as a secondary business mentioned that they benefit doubly from the shared agent network. Their income streams increased through earning extracommission andthey have also increased sales of other products from their primary businesses.
The customers, on the other hand, are particularly happy as the shared platform makes banking pleasant and convenient.In addition, they can receive services not just from the agent of their bank, but an agent from another bank.
Challenges facing the shared agent network
In an ideal scenario, on a shared agent platform, an agent should have just one point-of-sales device. However, since some banks have not yet signed onto the platform, there are still multiple devices from different providers deployed at the agentpoints. Nonetheless, given the complexities of managing the shared agent network device as well as devices of banks that are not on the shared network, some agents havedecided to have only one device and their choice is determined by the most responsive bank.
We found that several agents, despite being on a shared agent platform,still hold more than one point-of-sales device as even the banks on the shared platform continue to supply them with their own machines. This could be attributed to the fight amongst banks for visibility amongst the agents and tolet their customers avoid extra charges incurred from transacting through another bank’s agent.
During busy transactional banking seasons such as at the beginning of the school term, the system may go off-lineor slow down significantlydue to increased demand. In such instances, customers have to use other options available to them to transact.Some agents mention that they are hesitant to operate with just one machine on a shared platform on account of unreliable network and downtimes.
Some of the financial service providers feel that they lack control overpricing. They feel that the bigger banks on the platform influencepricing and they have no option but to follow.To understand this problem,consider the scenario explained below.
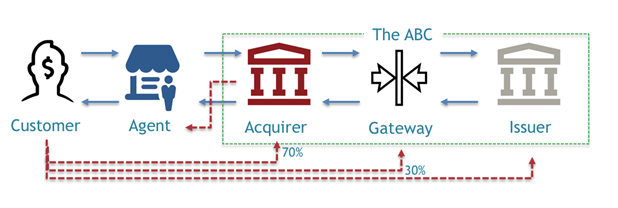
- In the shared agency network, the issuer bank (bank hosting customer account) pays 70% of the transaction fees collected from the customer to the acquirer bank (bank owning agent point)
- Of the 70%of the transaction fees earned,the acquirer pays a small percentageto the agent as commissions and keeps the remaining to meet the costs such as paper rolls, branding materials, as well as their profit margin
- The issuer on the other hand, whose customer did the transaction,gets 30% of the transaction fee. From this 30%, it pays half to ABC. Consequently, the issuerreceives 15% of the transaction fee.
As we can see from the description, the acquirer bank enjoysthe largest share from the transaction fee.It is worth noting that the transaction fee that will be charged is decided by the issuer bank, who owns the customer. Thus, the smaller banks feelthat such pricing approach favors that are often the acquirers due to their relatively larger agent networks. The decision on this percentage split was deliberate to favor acquirer banks in order to encourage bigger banks with larger existing agent networksto join the platform.
All financial products offered on the platform must be approved by ABC. Some of the financial service providers feel that the implementation of innovative ideas on the platformis limited by this requirement.
Lessons learned
The shared agent network in Uganda is still fairly young and the experiences of the FSPs and customers are still evolving. The stakeholders are addressing the challenges encountered as they come along. A few lessons learned so far include:
- Banks need to have uniform approaches to pricing. A bank that doesnot charge, or charges significantly lower, feeswhen its customers use its own agents, and charge higher for its customers to use agents of other banks will discouragethe use of the shared agent platform. In such a scenario, the reconciliation for agents becomesmuch more complicatedas theymanagemore than one single float account for the same bank.
- Pricing of a shared agent network is a complicated matter that should be carefully handled to provide financial services responsibly. Often providerscomplain of the uniform pricing structure as they have different cost structures.Thus, pricing is a delicate balance between what is reasonable to customers and what adequately compensates the banks and agents.
- Unless the banks feel that they own the model, there would be lower enthusiasm with which the shared agent network is embraced. In the case of Uganda, through the UBA, there is a perception that the banks collectively own the model, which motivates them to ensure that it succeeds.
- Excellent customer service is key to the success of a shared agent network. The agents have to be well recruited and trained. The banks are required to recruit agents that meet the set standards prescribed by the BoU. The agentsare expected to be courteous and professional as well asfollow the laid-out procedures to ensure consumer protection.Some of the measures put in place include refusal of the agents to conduct offline transactions, PIN authentication by both agent and customer for transaction approval, amongst others.
- There is a high likelihood of fraud being perpetrated on the platform due to the extension of several institutions’ and their customers’ information to third parties (agents). Prudent measures to strengthen data privacy through redaction of customer information that remains with agents is critical to preventing fraud.
According to the Finscope survey, 2018, only 58% of the Ugandan adult population own a bank account. This shows that there is a huge potential for growth. The ability of the agents and financial service providers on the shared platform to market the various accounts sold by the banks will be critical to ensuring that every Ugandan adult has a functional bank account. Overall,even though the COVID-19 pandemic has slowed down the progress being made due to the lockdowns instituted to manage the spread of the virus, agent banking in Uganda is headed in the right direction. ABC is in the process of revising its standard business rules that will govern all the banks on the platform. These revisions aim to harmonize and standardize the user experience, review the pricing regime as well as revamp the scheme rules to better manage the role of banks and agents in offering ubiquitous financial services in a responsible manner.
[WRITTEN BY Doreen Ahimbisibwe is the Manager Banking, Financial Services, Insurance, Microsave Consulting (MSC), Edward Obiko is Senior Manager – Digital Financial Services, MSC, and Anup Singh is Regional Head, Anglophone Africa, MSC ]













Leave a comment