In the world and Kenya, governments run professional police departments whose main job is maintaining law and order in the countries they are in.
These law enforcement agencies operate according to printed rules and regulations specifying their functions and powers, which vary from country to country because of differences in laws and constitutions governing them.
However, their duties are nearly similar – protecting life and property, handling and investigating crime and apprehending criminals.
Another similarity across the globe lies in the organisational structure of the police departments: Because of their crucial task of enforcing local laws and maintaining peace, most, if not all, have a chain of command based on ranks used to assign responsibilities to different personnel in service.
The police rank system, with high-ranking officials like police chiefs at the top, ensures each officer from way up to below receives proper direction to carry out their functions professionally and lawfully.
What are the ranks of police officers in Kenya?
Before we get started, it is worth knowing that the police officers in Kenya are under the National Police Service (NPS).
The main functions and objectives of NPS include striving for the highest standards of professionalism and discipline in Kenya’s police force by, among them, ensuring it complies with constitutional standards of human rights and fundamental freedoms in relation to their day-to-day discharge of duty to uphold police integrity and deter misconduct within the service. That is why, within its composition, it has the Internal Affairs Unit (IAU) that receives and investigates complaints against police officers.
Aside from the Internal Affairs Unit, the National Police Service of Kenya has three other departments, which are the Kenya Police Service, the Administration Police Service, and the Directorate Criminal Investigations (DCI), all headed by one Inspector General whose duty is mainly overseeing the implementation of policy decisions and coordinating and auditing all police operations for effective policing. So, the Inspector General is the highest-ranking officer and the boss of the Kenyan police.
The other departments, the Kenya Police Service and the Administration Police Service (popular or unpopular as AP-s), below the Inspector General, each are under different Deputy Inspector Generals who perform their duties under the command and control of the Inspector General.
The officers in the remaining two – the DCI and the Internal Affairs Unit, are under the leadership of directors – the Director of Criminal Investigations and the Director IAU, respectively. However, they also receive orders from the Inspector General, but their divisions have different ranking structures than the Kenya Police Service and the Administration Police Service.
The ranking structure in the Kenya Police Service and the Administration Police Service is nonetheless the same, excluding the Inspector General, who is the overall head and the fact that the entire National Police Service has only one Inspector General, now Japhet Koome, at any given time. Their ranks in order are:
1. Inspector General
2. Deputy Inspector General
3. Senior Assistant Inspector General
4. Assistant Inspector General
5. Commissioner
6. Senior Superintendent
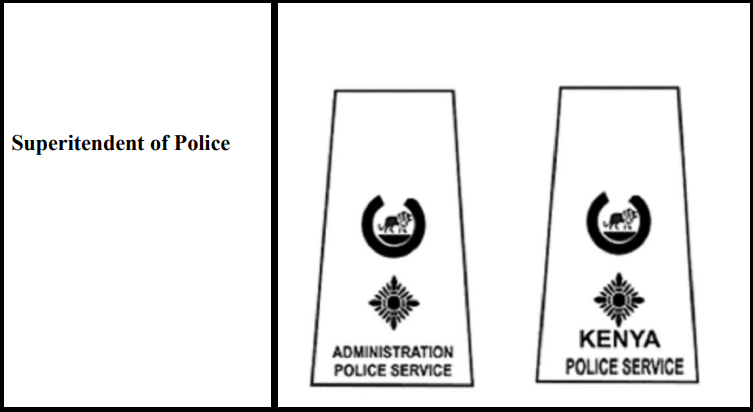
7. Superintendent of Police
8. Assistant Superintendent
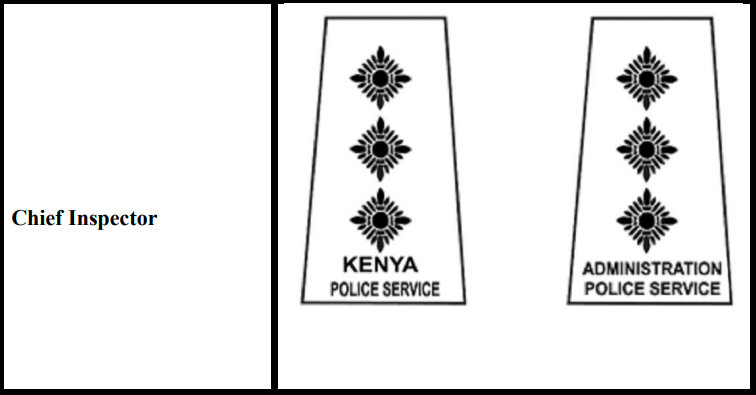
9. Chief Inspector
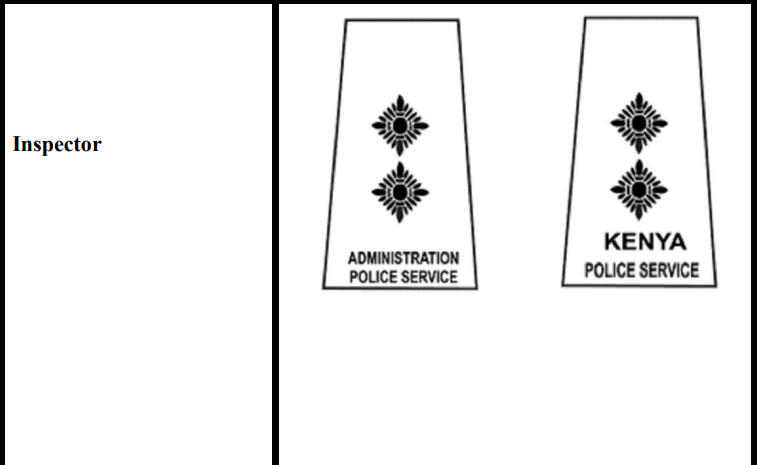
10. Inspector
11. Senior Sergeant
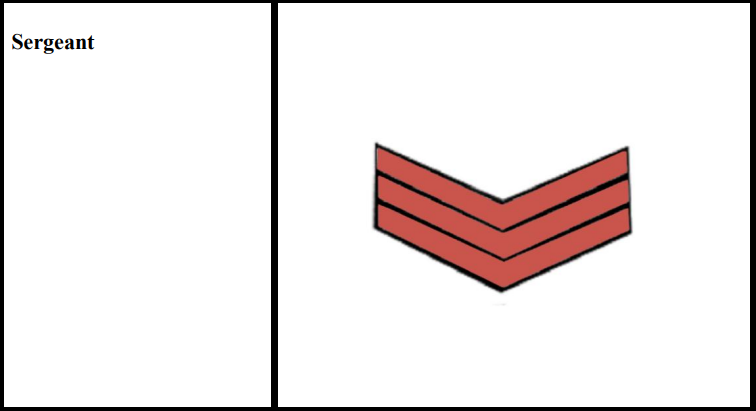
12. Sergeant
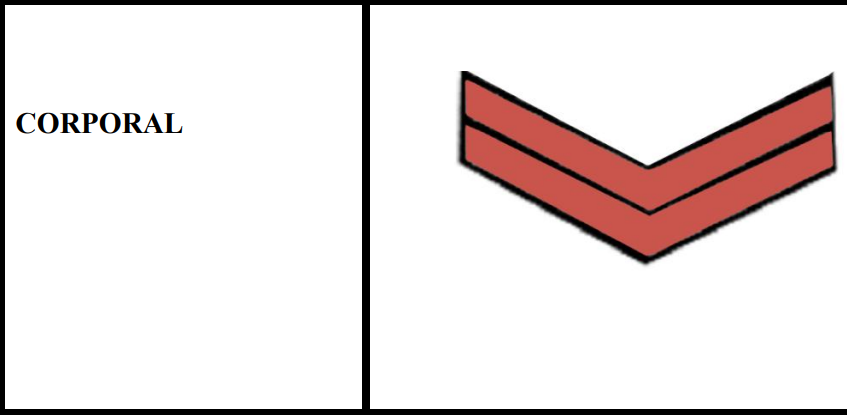
13. Corporal
14. Constable
The above are the 14 ranks, from the highest to the lowest, that you will find within the Kenya Police Service and the Administration Police Service.
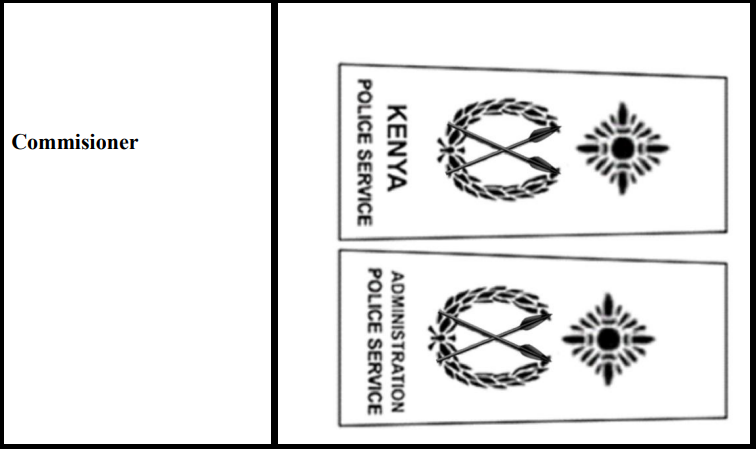
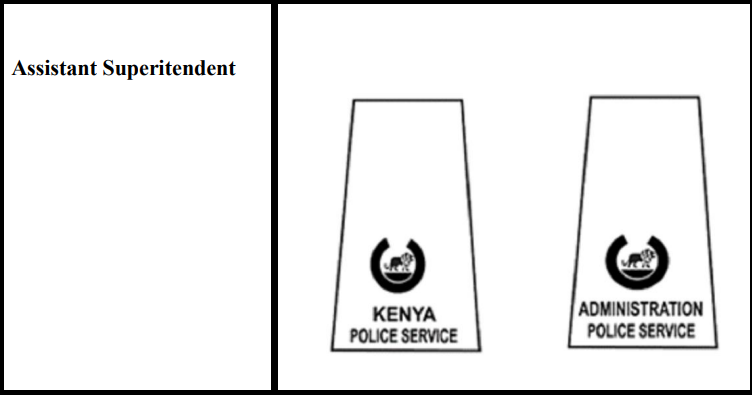
Even so, across these two police divisions, as the Police Grades, the shoulder badges of the officers differ except for the Inspector General, whose special insignia has unique gorget patches and the lanyard is embellished with the National Police Service colours but not specifics as in either the Administration Police Service or Kenya Police Service. See;

Kenya Police Service badges of ranks and insignia – in photos

Distinguish how the badges of officers in the Kenya Police Service and the Administration Police Service of the NPS vary, from rank to rank, starting from the Deputy Inspector General at the top of each unit to the corporal rank in the lower part of the chain of command because the lowest rank of constables has no shoulder insignia:
* Insignia of Deputy Inspector Generals

* Insignia of Senior Assistant Inspector Generals

* Insignia of Assistant Inspector Generals

* Insignia of Commissioners of Police
* Insignia of Senior Superintendents

* Insignia of Superintendents of Police

* Insignia of Assistant Superintendents
* Insignia of Chief Inspectors
* Insignia of Inspectors
* Insignia of Senior Sergeants

* Insignia of Sergeants
* Insignia of Corporals
* Insignia of Constables
As said, a police constable has no shoulder insignia in Kenya.
Read: How to Become a Traffic Police Officer in Kenya












What are the requirements for one to be promoted to another rank ,we have got so many old men and women in our services who are still holding a constable and corporal ranks and they are almost getting to their retirement period,enlighten the public how this happen